DMARC record setup guide
Check your domain for DMARC, DKIM, SPF and MX records. Get a free report.
- The impact of Business Email Compromise
- A quiet Google update just made SPF more forgiving
- Cyber Insurance and DMARC Enforcement
- Email impersonation scams explained
- TLS-RPT Record
- 🇩🇪 Welche Hosting Anbieter unterstützen DMARC
- Reverse Engineering Phishing
- DMARC Enforcement in 2026
- DMARC for non sending domains
- Manual DMARC Monitoring vs Automated Monitoring
- SMTP Smuggling
March 19, 2024
Have you ever received a suspicious email that looks like it came from your bank or favorite online store? If that’s so, you're not alone. The ease of email comes with risks.
Email spoofing and phishing attacks have become rampant and they target individuals and businesses. Email authentication protocols such as DMARC, SPF, and DKIM are important to cope with this.
What is DMARC?
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. It's a security pistol that helps you prevent email-based attacks, such as email spoofing and phishing.
DMARC puts an end to verification as it verifies the alignment of SPF and DKIM. It also provides you with a reporting mechanism that gives you track of your email performance.
It helps domain owners and businesses and defines how email providers should handle messages.
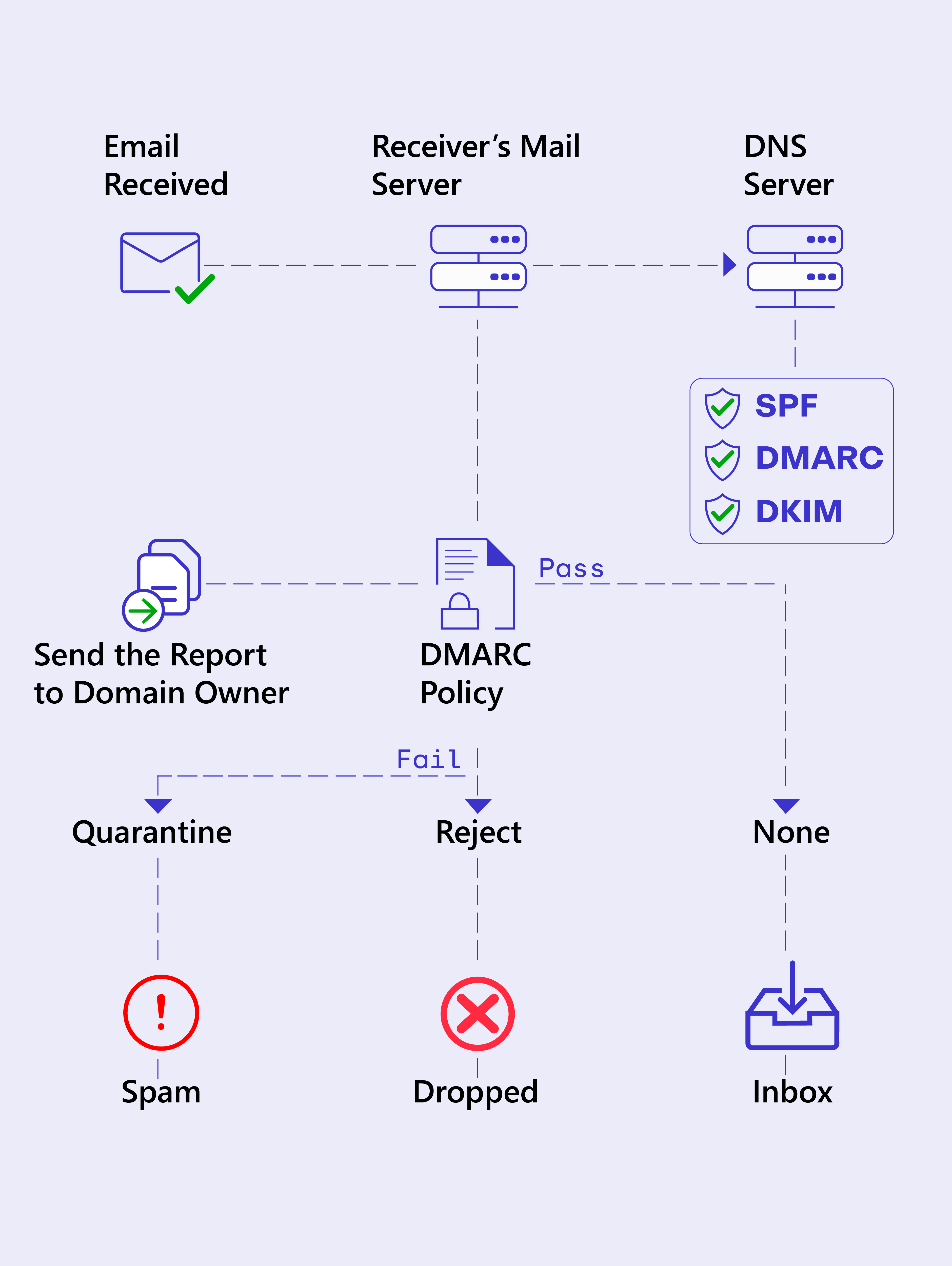
How DMARC Works? How DMARC Protects Your Domain from Spoofing and Phishing
DMARC looks at two other security protocols that are SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). These protocols are also made to prevent email faking.
SPF checks if the server sending the email is authorized to do so.
DKIM ensures that the email is genuine and hasn't been altered by adding a digital signature.
SPF and DKIM Authentication
The receiving email server checks the SPF record to see if the email comes from a legitimate IP address. Then, it checks the DKIM signature to ensure the email isn’t altered in transit.
DMARC Verification
After SPF and DKIM, DMARC steps in. It checks whether your email aligns with both SPF and DKIM rules. This is called "alignment." DMARC ensures that the "From" address in the email header matches the domain in the SPF and DKIM checks. If everything lines up, this means your email is authentic.
DMARC Policy
If the email passes, it's then delivered to the recipient. But what if something doesn't match up? This is where your DMARC policy comes into play. You, as the domain owner, can tell DMARC what to do when an email fails these checks:
None: Takes no action but reports the failure.
Quarantine: Sends the email to the recipient's spam or junk folder.
Reject: Blocks the email altogether so it never reaches the inbox.
Report
One of DMARC's finest features is its reporting system. DMARC sends a report to the domain owner which shows all the attempts to send emails from your domain. This step helps to ensure that the email is legitimate.
Why does DMARC matter?
Without DMARC, suspicious emails might reach your customers' inboxes. This results in confusion or potential data breaches.
DMARC works as the final piece of a puzzle that includes SPF and DKIM. It analyzes the results of SPF and DKIM and depends on your policy. It either lets the email through or stops it in its tracks.
How to Generate and Lookup DMARC record?
If you want to generate or check your existing DMARC policy, DmarcDkim.com is an excellent tool. You enter your domain name and the tool gives you a detailed report of your DMARC setup.
How to Locate DMARC Records in DNS Lookups?
DMARC records are stored in your domain's DNS settings. DNS works like the phonebook of the internet. It tells other servers where to find different things that include your DMARC settings. Here's how you can find them:
Access Your DNS Records Start by logging in to your DNS management platform. You can do this through your domain registrar or a hosting provider.
Look for TXT Records DMARC records are stored as TXT (text) records in your DNS settings. Search for any TXT records starting with "_dmarc." The format looks like this:
Go for the Correct Setup Once you've located the DMARC record, it’s time to check if it's configured correctly. You can look for important tags like v=DMARC1 (version), p= (policy), and rua=. If you don't see these it means DMARC isn't set up yet.
Basic DMARC Syntax
A DMARC record starts with a version tag and is followed by different tags. The tags define the policy for your domain. Here’s a basic example of a DMARC record:
v=DMARC1: This specifies the version of DMARC that’s used. Presently, the only version is DMARC1, so you’ll always see this at the beginning of the record.
p=reject: This is the policy tag. It tells receiving email servers what to do with emails that fail the DMARC check. In this case, it’s set to reject emails that don’t pass.
rua=mailto @yourdomain.com: This tag specifies the email address where you want to receive aggregate reports about your DMARC performance.
ruf=mailto @yourdomain.com: This is for forensic reports that provide more detailed information about failed messages.
What Are DMARC Policy Tags?
Tag |
Description |
Column |
v |
Version of DMARC protocol. This will always be DMARC1. |
v=DMARC1 |
p |
Policy for messages that fail DMARC checks: none, quarantine, or reject. |
p=reject |
sp |
Subdomain policy. This defines a separate policy for subdomains if needed. |
sp=quarantine |
rua |
Aggregate reports URI. Where to send daily aggregate reports. |
rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@domain.com |
ruf |
Forensic reports URI. Where to send detailed forensic failure reports. |
ruf=mailto:forensics@domain.com |
pct |
Percentage of emails to apply the DMARC policy to (0-100%). |
pct=100 |
adkim |
Alignment mode for DKIM (r for relaxed, s for strict). |
adkim=s |
aspf |
Alignment mode for SPF (r for relaxed, s for strict). |
aspf=r |
Conclusion
If you receive malicious emails there’s a high chance of personal data theft, financial fraud, or even identity theft. The solution is that you implement DMARC, SPF, and DKIM. It helps you create a safer digital environment for your business and customers.
FAQs
Who Requires DMARC? DMARC is essential for any organization that sends emails from its domain. If you want to protect your brand, customers, and reputation from email spoofing or phishing attacks, DMARC is a must.
Is DMARC Better Than SPF? DMARC, SPF, and DKIM work together for complete email security. SPF alone only checks if an email comes from an authorized server but it doesn't stop all forms of spoofing.
Does Gmail Use DMARC? Yes, Gmail supports and uses DMARC for sending and receiving emails. Gmail also encourages domain owners to implement DMARC, SPF, and DKIM to prevent email spoofing.
Is DMARC Free? Yes, DMARC is free to implement! Most domain check tools allow you to set up DMARC records at no extra cost, like Dmarcdkim.com. It also provides you with futuristic reporting and analysis. If you want a personalized consultation, contact DmarcDkim.com to get a quote today.
Setup Help Scout SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records for Domain Authentication
Authenticating and securing email communication is crucial for businesses to prevent spoofing and improve deliverability. There are three commonly used protocols to authenticate emails - SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKey Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance ).
Read more →Salesforce DMARC, DKIM and SPF Configuration - Domain Authentication Guide
If you are tired of emails going to the spam, this article is for you. It will guide you on how to setup Salesforce SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for email domain authentication
Read more →How to Setup Google Workspace SPF, DKIM, DMARC, MX Records - Email Authentication Tutorial
If you are tired of emails going to customers' spam folders, this article is for you. The inbox providers like Google and Yahoo only approve emails that pass their authentication check. Therefore, it is important to comply with the security standards to be trusted by inbox providers. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are commonly used authentication standards to verify your domain. You can find these records in the Google Workspace Gmail settings. Follow the steps below to configure and add the Google Workspace verification records to the DNS provider.
Read more →Setup Microsoft 365 DMARC, DKIM, SPF for Domain Authentication
Email authentication is a set of standards that ensure your emails come from a legitimate source and are safe to open by the recipient. This method prevents your domain from being spoofed and scammed.
Read more →Resend SPF, DKIM, DMARC Configuration - Step-by-Step Guide
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) helps prevent email spoofing by allowing domain owners to specify which mail servers are authorized to send email on behalf of their domain.
Read more →How to configure DMARC, DKIM and SPF DNS records in GetResponse?
DKIM and SPF records are of paramount importance when it comes to efficient email communication. These DNS records verify the sender's identity and email authenticity. DMARC adds further security to your webmail by setting additional rules for email communication.
Read more →Configure SPF, DKIM, Return-path records in MailerSend
Friendly for users, hard on spammers - MailerSend has earned it's spot among top reliable email delivery platforms. Not only email delivery, MailerSend also provides domain authentication services. It generates DNS records that give your emails a unique signature, making it spam proof.
Read more →Setup Email Sender Signatures in Postmark
Setting Sender Signature mean giving your email a unique identity that make it difficult for spammers to impersonate as you. Email platforms like Gmail, Yahoo, and outlook require sender verifications to ensure emails are coming from the legit domain owner and are safe for readers to open. There are many email delivery platforms that provide DNS records in order to protect your emails from spoofing and forgery. Postmark is one of them. Its interface is quite simple and its services are trustable. In this guide post, we'll walk you through the easy steps of webmail authentication process. So let's start!
Read more →Adding DNS records for Mailchimp DMARC, DKIM and SPF
MailChimp, one of the trusted email delivery services, helps with email campaigns and authenticates your domain to minimize spoofing. Domain authentication is the number one strategy to avoid emails ending in the spam folder.
Read more →
Check domain and follow the instructions to nail down your DMARC configuration.
No expert knowledge needed!