Email is one of the most important communication tools for your business. Another part of this process is named as MX (Mail Exchange) record. Without properly configured MX records, your email delivery can fail, and your messages can be lost.
MX records are part of the Domain Name System (DNS) and direct incoming emails to the correct mail server. If you set them up incorrectly, your emails may not reach the recipient. For your business this can mean lost communication, decreased productivity, and even missed opportunities.
What Is an MX Record?
An MX record is a DNS record that tells you which mail server is responsible for receiving emails for a domain. When you send an email, the server checks the recipient’s MX records to know where to deliver the message.
Functions of MX Records:
Identifies the mail server that handles email for a domain
Ensures emails are routed efficiently to the correct destination
Work alongside SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) for email transmission
How MX Records Differ from Other DNS Records?
MX records are unique because they specifically handle email routing. Here’s how you can know the difference:
A Record: Maps your domain to an IP address for website hosting.
CNAME Record: Creates an alias for a domain.
TXT Record: Stores text-based information like SPF and DKIM for email security.
MX records are used for email traffic. Without a properly configured MX record, email servers will never know where to send messages.
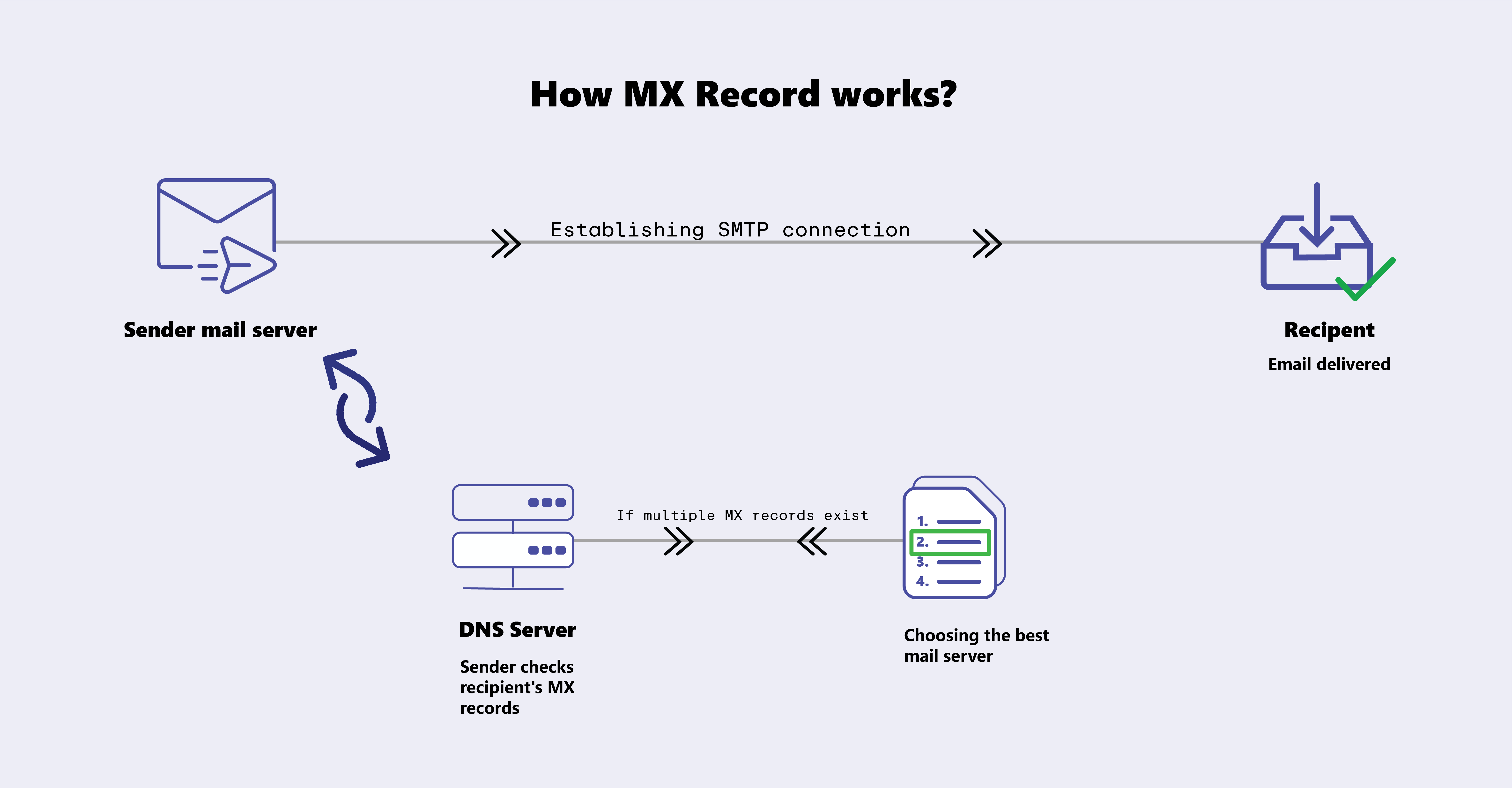
How MX Records Work?
When you send an email the server follows a step-by-step process to deliver it.
The Email Routing Process:
DNS Query: The sending email server looks up your recipient domain’s MX records.
Priority Selection: If multiple MX records exist, the server selects the one with the highest priority.
SMTP Connection: Your server connects to the recipient’s mail server via SMTP.
Message Delivery: The email gets transferred and processed by the recipient’s mail server.
MX Record Priority and Multiple Mail Servers
Your MX record has a priority value (also called a preference number). Lower values indicate higher priority. This helps email servers decide which mail server to use first.
For example:
MX 10 – Primary mail server (used first)
MX 20 – Backup mail server (used if the primary is down)
MX 30 – Secondary backup server
Why Multiple MX Records Are Important?
Multiple MX records provide email redundancy. If your primary mail server fails, your emails automatically get routed to the next available server and prevent lost messages.
How to Check and Verify MX Records
If you want to ensure email reliability, make sure to regularly check and verify your MX records. These are methods to check MX Records:
Command-line tools:
nslookup -type=MX domain.com (Windows)
dig MX domain.com (Linux/macOS)
Online DNS lookup tools: Websites like DMARCDKIM.com provide real-time MX record checks.
How to Set Up MX Record
If you want to configure an MX record, you should do it the best way for reliable email delivery. Follow these steps:
1. Access Your Domain’s DNS Settings Log into your domain registrar or hosting provider (e.g., GoDaddy, Cloudflare, Namecheap).
2. Add an MX Record
Host: Your domain name (e.g., example.com)
Value: The mail server address (e.g.example.com)
Priority: Lower numbers indicate higher priority
TTL (Time to Live): Recommended: 300 seconds to 1 hour
3. Save and Propagate Your Changes DNS changes can take a few hours to propagate. Use tools to confirm updates.
Backup MX record
A backup MX record is an additional Mail Exchange (MX) record configured with a lower priority value that helps you as a failover option when the primary mail server is unavailable.
When you send an email, the mail server queries the recipient’s MX records in order of priority. If the primary mail server is down or unreachable, your email is routed to the backup mail server specified in the secondary MX record. This increases your email continuity and reduces the risk of your lost or delayed messages.
You can use Backup MX records to maintain reliable email delivery, during server maintenance, outages, or high traffic loads. Proper configuration is important to prevent bounced emails.
Common MX Record Issues You May Face
1. Misconfigured MX Records
Incorrect MX record configuration can cause email failures. Always double-check priority values and server addresses.
2. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Conflicts
These security protocols authenticate your emails but may conflict with your MX records if you do not configure them properly.
3. Emails Marked as Spam
Go for seeing blacklisted IPs and ensure your authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) are correctly implemented.
MX Records and Email Security
MX records don’t directly secure your emails, they help you in email authentication and spam prevention.
MX Records Improve Security:
Ensure emails are routed to your authorized mail servers.
Work with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent phishing and spoofing.
Help detect unauthorized senders trying to use your domain.
Best Security Practices:
You should use a reliable email provider with strong security policies.
Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC correctly.
Regularly monitor your MX records to prevent unauthorized changes.
FAQs
Can I have a domain with multiple MX DNS records? Yes, multiple MX records provide you with redundancy and reliability.
What happens if an MX record is missing? Without an MX record, your emails won’t be delivered to that domain.
How do MX records affect email forwarding? Incorrect MX settings cause forwarded emails to fail or get flagged as spam.
Can MX records be used for subdomains? Yes, MX records can be set up for subdomains.
Conclusion
MX records are important for a good and secure email delivery. A properly configured MX record makes sure that your emails reach their destination without errors.
More articles
Check domain and follow the instructions to nail down your DMARC configuration.
No expert knowledge needed!