CNAME record setup guide
Check your domain for DMARC, DKIM, SPF and MX records. Get a free report.
- The impact of Business Email Compromise
- A quiet Google update just made SPF more forgiving
- Cyber Insurance and DMARC Enforcement
- Email impersonation scams explained
- TLS-RPT Record
- SMTP Smuggling
- 🇩🇪 Welche Hosting Anbieter unterstützen DMARC
- Manual DMARC Monitoring vs Automated Monitoring
- Reverse Engineering Phishing
- DMARC Enforcement in 2026
- DMARC for non sending domains
March 23, 2024
A CNAME (Canonical Name) record is an important part of your Domain Name System (DNS) that helps you point one domain name to another. Instead of linking a domain directly to an IP address, it helps you to redirect traffic to another domain.
This makes domain management simpler and more flexible for you. You can use it as a business owner, a developer, or a website owner frequently. CNAME records help you to manage your subdomains and integrate third-party services.
How CNAME Records Work?
When you enter a domain name, the DNS resolver checks for any linked records. If it finds a CNAME record, it goes with the pointer to the specified target domain. The DNS lookup continues until it reaches an A record, which translates your domain into an IP address.
Once your IP address is identified, the browser makes a connection with your server that hosts the website. This entire process happens in milliseconds and it’s a smooth experience.
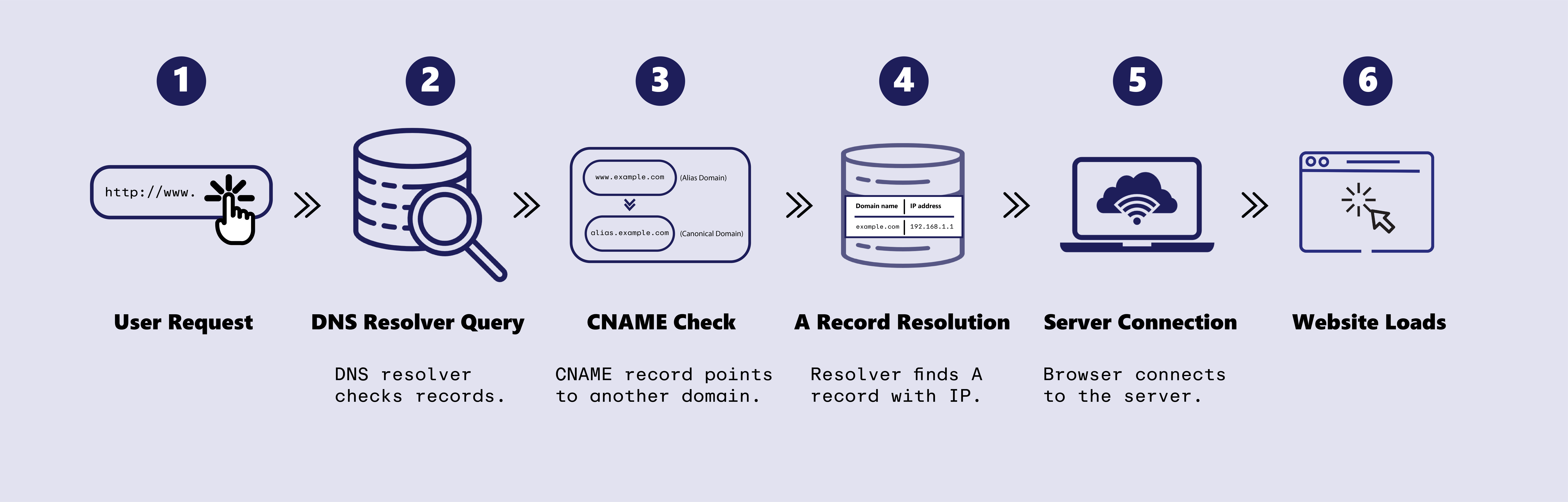
CNAME vs. A Record: What’s the Difference?
CNAME and A records are important for your DNS configurations. They have different purposes. You can use it for subdomains and to balance load.
An “A” record directly helps you map your domain to an IP address. This is good for root domains that cannot use CNAME records.
If your website requires a static IP, “A” record is the right choice for you. However, if you need flexible and easier domain management, you can go with a CNAME record.
What’s the CNAME Record Format?
A CNAME record has a specific structure in your Domain Name System (DNS). The format has got following elements:
What’s the Basic Syntax:
[subdomain] [TTL] IN CNAME [target domain]
Components:
Subdomain: The alias domain that points to another domain
TTL (Time to Live): It works as an option and it helps you define how long the record is cached.
IN: This works as a short form for "Internet" and is required in DNS records.
CNAME: Helps you specify that this is a Canonical Name record.
Target Domain: It is the actual domain that the alias resolves to.
Example of CNAME Record:
www is an alias for example.com.
The record tells you that DNS resolves to direct requests for www.example.com to example.com.
3600 seconds is the cache time.
What Are Some CNAME Practices You Need To Follow?
Your CNAME record should never point to an IP address.
Root domains cannot use CNAMEs.
You need to avoid CNAME loops and do not point a CNAME to another CNAME indefinitely.
Where Can You Use CNAME Records?
You can use CNAME records in domain management to create aliases. They are useful when you need to manage multiple domains under a single service. You can use it for content delivery network (CDN), email services, or even website hosting.
One of the most common applications you can have is redirecting subdomains to the main domain without the need for separate hosting configurations.
For example, if your company wants "blog.example.com" to point to "example.com," the CNAME record makes sure that any updates to the main domain automatically apply to the subdomain as well. CNAME records also help you to integrate third-party services like email providers and cloud platforms.
This helps you with seamless redirection without altering DNS settings repeatedly.
How Can You Create a CNAME Record?
If you want to set up a CNAME record. It's a simple process. You can do it through your domain registrar or DNS hosting provider.
Log in to your domain management account and navigate to the DNS settings or DNS management section.
Look for an option to add a new record and select "CNAME" as the record type.
In the "Name" or "Host" field, enter the subdomain you want to alias, such as "www" if you're pointing "www.example.com" to another domain.
Next, in the "Value" or "Target" field, enter the destination domain to which your CNAME should point.
Save your record and allow some time for DNS propagation. This can take a few minutes to 48 hours.
Once your record is active, your subdomain will automatically resolve to the target domain. This helps you get a seamless redirection without manual updates to the IP address.
What are Disadvantages of CNAME Records?
There are multiple advantages of CNAME records, but you can come up with specific restrictions as well. You cannot use CNAME records for root domains. Those require an A record. Moreover, CNAME records cannot coexist with your MX records which are important for your email delivery.
If you use CNAME records without proper instructions, it can also slow down your DNS resolution. It ensures correct configurations and prevents performance issues and can also help you enhance domain stability.
CNAME Record Issues
Misconfigured CNAME records can cause website downtime and redirection failures.
One issue is CNAME loops in which a record mistakenly points to itself. This creates an endless DNS resolution cycle. Another problem you may face is when a CNAME record points to a non-existent domain. This leads you to broken links and errors.
If changes do not take effect on your website immediately, DNS propagation delays may be the cause. It clears your DNS cache or uses tools that help you verify record updates.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a CNAME Record Point to Another CNAME Record? Yes, but it's generally discouraged because multiple lookups can slow down your DNS resolution.
Does a CNAME Record Affect SEO? CNAME records themselves do not harm SEO, but improper configurations can lead to indexing issues or duplicate content problems.
Can a Domain Have Multiple CNAME Records? No. A domain cannot have multiple CNAME records but different subdomains can each have their own CNAME records.
Is a CNAME Record the Same as a Redirect? No. A CNAME record is a DNS-level mapping and an HTTP redirect is a web server function that forwards traffic.
Conclusion
CNAME records are important for your domain management and you can handle subdomains, third-party integrations, and website optimizations flexibly. They help you simplify domain configurations and reduce maintenance efforts. This makes them invaluable for businesses and website owners.
How to Configure HubSpot DMARC, DKIM, SPF Domain Authentication?
HubSpot, a leading CRM and marketing email service provider, allows you to authenticate your emails within a few steps. Simply connect your domain with HubSpot and it generates DNS records. By adding these records to your DNS provider, you can authentication your domain.
Read more →
Check domain and follow the instructions to nail down your DMARC configuration.
No expert knowledge needed!