Domain Authentication setup guide
Check your domain for DMARC, DKIM, SPF and MX records. Get a free report.
- The impact of Business Email Compromise
- A quiet Google update just made SPF more forgiving
- Cyber Insurance and DMARC Enforcement
- Email impersonation scams explained
- TLS-RPT Record
- SMTP Smuggling
- 🇩🇪 Welche Hosting Anbieter unterstützen DMARC
- Manual DMARC Monitoring vs Automated Monitoring
- Reverse Engineering Phishing
- DMARC Enforcement in 2026
- DMARC for non sending domains
March 11, 2024
Domain authentication works as an ID check for your emails. It’s a way to prove that an email you’ve received is from the domain it says it’s from. When you send an email, domain authentication helps email servers verify that you’re real and not a scammer.
Email is a way for businesses to communicate. But without domain authentication, anyone can pretend to be you. Scammers can send fake emails from your domain, they can trick your customers and damage your reputation.
If your emails aren’t properly authenticated, they might end up in the spam folder or even worse, someone may use them in phishing attacks. No business wants that.
What Happens Without Domain Authentication?
Without domain authentication, email providers don’t know if the emails coming from your domain are legit. That’s why your messages get flagged as spam or even blocked. This can hurt your business, especially if important emails don’t make it to your customers. If someone uses your domain to send phishing emails, your reputation could be damaged.
How Does Domain Authentication Work?
When your email is sent, email servers at the receiving end check its authenticity by using your domain’s DNS records. These records tell the server whether the email is from a legitimate source or if it's someone trying to spoof your domain.
DNS and email servers Every time an email is sent from your domain, the receiving email server looks up your domain’s DNS (Domain Name System) records. These records contain the rules and settings that show which servers are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain. If the records don’t match up, the email gets flagged as suspicious or sent to spam.
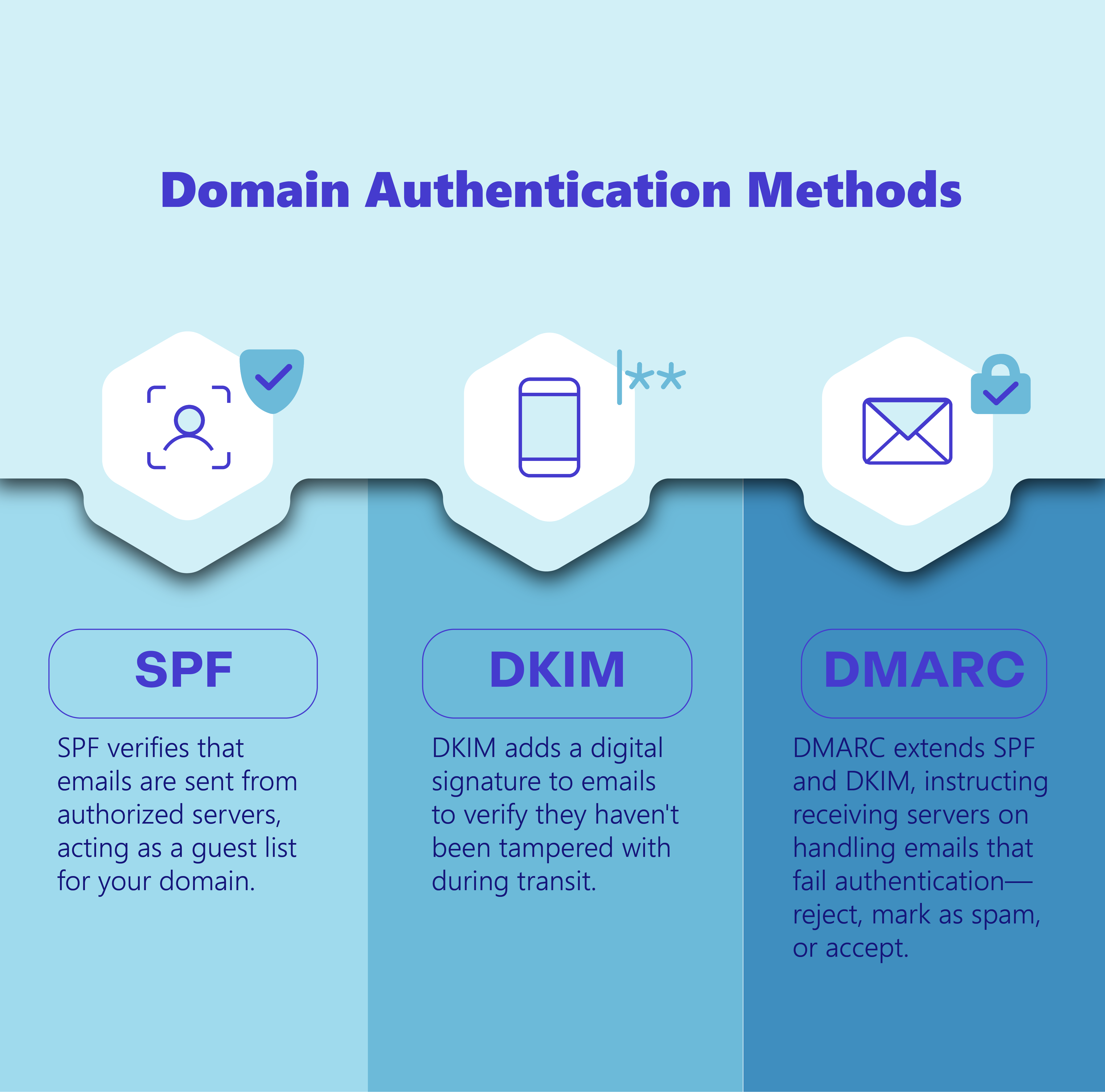
Common Methods of Domain Authentication
There are three main methods for authenticating your domain: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
These work together to ensure your emails are legitimate and protect your domain from being used by spammers or scammers.
DMARC ties both of them together, ensures alignment and provides instructions about what to do if an email fails to authenticate. This way you are able to secure the integrity of your emails and avoid any spoofing.
1. SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF checks if an email is being sent from an authorized server. It’s like a guest list for your domain. Only the servers listed in your SPF record are allowed to send emails on your behalf.
How to verify SPF: Use online tools like DmarcDkim.com to check if your SPF record is set up correctly. You can also manually check it through your DNS settings.
Common errors: Misconfigured SPF records such as missing authorized IPs or servers can cause your emails to fail authentication. Moreover, if your SPF record is too long or not updated, it can lead to issues.
2. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM ensures that an email hasn’t been tampered with during transit. It adds a digital signature to your email header which then receives server checks to make sure everything’s legitimate.
How to verify DKIM: Use a DKIM validator tool to confirm that your emails are properly signed. The tool checks the signature against the public key stored in your DNS.
Common errors: DKIM can fail if the signatures don’t match due to improper setup or if the email content is altered. Inconsistent or missing DKIM records can also cause verification issues.
3. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
DMARC builds on SPF and DKIM which conveys to receiving servers how to handle emails that fail authentication. You can choose to have them rejected, marked as spam, or accepted based on your DMARC policy.
How to verify DMARC: Use the DmarcDkim.com DMARC checker tool to generate or verify your DMARC policy. This tool also helps you ensure your SPF and DKIM align properly.
Common errors: Misconfigured DMARC policies such as overly strict settings or incomplete records can cause legitimate emails to be rejected. Always review your DNS to make sure all records are accurate and up-to-date.
DMARC Reporting
DMARC has evolved beyond just being a basic email authentication protocol. Now it has advanced features that significantly enhance its functionality. One of the standout features is its powerful reporting capabilities.
DMARC provides two types of reports: aggregate and forensic.
Aggregate reports offer an overview of how emails from your domain are being processed by recipient servers. This helps to know which message passes or fails authentication. This information is invaluable for identifying trends and potential vulnerabilities in your email practices.
DMARC reporting helps businesses enhance their visibility, this helps to protect their brand reputation. It also allows business owners to make informed decisions and adjust to DMARC policies. This levels up their email security and authentication strategy. In this way, only legitimate emails get delivered and fraudulent emails get blocked.
Forensic reports, on the other hand, provide detailed insights into individual authentication failures. This helps you to see exactly what went wrong with specific messages. This level of transparency helps businesses pinpoint weaknesses in their email security.
FAQs
What happens if you don’t set up domain authentication? Without domain authentication, your emails are more likely to be flagged as spam or blocked altogether. Moreover, scammers can use your domain to send phishing emails, harm your reputation, and put your customers at risk.
How can I fix SPF/DKIM/DMARC errors quickly? You can start by using online tools like DmarcDkim.com to pinpoint where things are going wrong. Make sure your DNS records are up-to-date and add any missing IPs or correct misaligned signatures. Most errors come from misconfigurations, so double-check the setup.
Is domain authentication necessary for small businesses? Absolutely. No matter the size of your business, domain authentication protects your brand and ensures your emails are delivered. Even small businesses can be targeted by phishing attacks, so securing your domain is a smart move.
Final Thoughts
When you set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC correctly, they protect your brand and customers. These authentication methods work flawlessly to prevent your domain from getting hijacked by cybercriminals. One thing that you can help yourself with is avoiding common errors and keeping your records updated.
Configure E-goi SPF, DKIM, DMARC Records - Domain Authentication Guide
This article will guide you how to authenticate the E-goi domain for sending.
Read more →How to Configure DMARC, DKIM & SPF Authentication in Rapidmail?
Rapidmail, a German Newsletter Software, allows you to add an extra layer of security to your newsletters to prevent spamming. It provides SPF and DKIM records for your sender domain so you can add these records to the DNS of your hosting server.
Read more →How to Achieve Mailjet DMARC Alignment with SPF & DKIM?
Authenticating and securing email communication is crucial for businesses to prevent spoofing and improve deliverability. There are two commonly used methods to authenticate emails - SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKey Identified Mail). You can get the SPF/DKIM values from the email service provider and add them to the domain hosting server to authenticate your webmail.
Read more →
Check domain and follow the instructions to nail down your DMARC configuration.
No expert knowledge needed!